glassdbase
Content
(1) Experimental techniques for optical characterization of glasses
See also 'Reports' on home page for more technical details. Data evaluation is based on the 'European Standard EN 410: Glass in building - Determination of luminous and solar characteristics of glazing.'
Measured quantitiesAngular resolved spectral transmittance and reflectance
Derived optical quantities
- solar direct transmittance, reflectance, and absorptance
- color of transmitted and reflected daylight
- color rendering of test colors
Method of measurementThe insulating glass unit (or individual glass panes) mounted on a revolving support is irradiated by a light source. The transmitted or reflected light enters a collimator and the spectral distribution of the light intensity is measured by diode array spectrometers.
The angular dependent measurements are enabled by rotating the glass and by defining the angle of light incidence by the collimator. The laterally extended, homogeneous light source ensures that contributions by higher order beams transmitted through the glass by multiple reflections between the glass panes are taken into account.
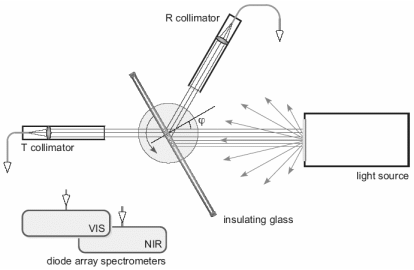
Data evaluationThe angular resolved transmittance and reflectance spectra are used to calculate all one-figure parameters typically used for optical characterization of insulating glass units. The colors of transmitted and reflected daylight are characterized as a function of the angle of the incident light as well as the rendering of test colors according to EN 410.
(2) Thermal measurements for total solar energy transmittance (solar factor) determination
See also 'Reports' on home page for more technical details. Data evaluation is based on the 'European Standard EN 410: Glass in building - Determination of luminous and solar characteristics of glazing.'
Measured quantitiesRise of outer and inner surface temperatures under irradiation in a solar simulator.
Derived quantitiesBy making use of the knowledge of the absolute optical absorptance along with the temperature measurements the following quantities are calculated according to EN 410:
- angular dependent secondary internal heat transfer factor qi
- angular dependent total solar energy transmittance (solar factor) g.
Method of measurementThe insulating glass unit is irradiated in a solar simulator by a spectral radiation close to the solar spectrum. The rise of the outer and inner surface temperatures in the steady state are used to calculate the outer and inner heat flows under laboratory conditions, i.e. in quiescent air.
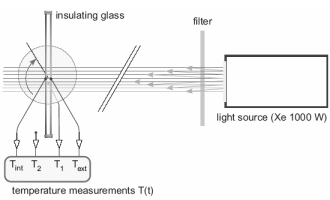
Data evaluationThe as obtained absolute heat flows are then used in order to calculate the secondary internal heat transfer factor qi and the total solar energy transmittance (solar factor) g for standard conditions as defined in EN 410.
(3) Dynamic temperature simulation of a standard room by using the total solar energy transmittance (solar factor)
See also 'Reports' on home page for more technical details. Data evaluation is based on the 'European Standard EN 410: Glass in building - Determination of luminous and solar characteristics of glazing.'
Input parameterExperimentally determined angular dependent total solar energy transmittance (solar factor) obtained from experiments (1) and (2).
Simulated quantityThe internal temperature evolution of a standard room during a climatic episode with clear sky is calculated. The maximum temperature rise is used in order to compare the relative performance of different sun protection glasses.
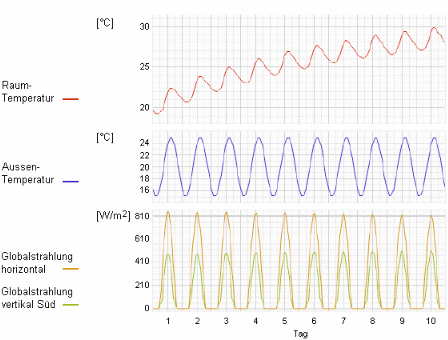
Model descriptionA standard room with an initial temperature of 20°C oriented south is subjected to a prolonged fair weather period in summertime. The model simulates temperatures dynamically i.e. the heat capacity of construction elements is taken into account. The temperature evolution reveals the asymptotic approach to a final temperature and the superimposed daily variations. The maximum temperature obtained at the end of the 10-days simulation period can be used as a measure for the total solar heat load for the considered glass type.
The simulation is fully based on the angular dependent total solar energy transmittance (solar factor) as obtained from experiments (1) and (2).